This is a viewer only at the moment see the article on how this works.
To update the preview hit Ctrl-Alt-R (or ⌘-Alt-R on Mac) or Enter to refresh. The Save icon lets you save the markdown file to disk
This is a preview from the server running through my markdig pipeline
When developing software traditionally we'd spin up a database, a message queue, a cache, and maybe a few other services. This can be a pain to manage, especially if you're working on multiple projects. Docker Compose is a tool that allows you to define and run multi-container Docker applications. It's a great way to manage your development dependencies.
In this post, I'll show you how to use Docker Compose to manage your development dependencies.
First you'll need to install docker desktop on whatever platform you're using. You can download it from here.
NOTE: I've found that on Windows you really need to run Docker Desktop installer as admin to ensure it installs correctly.
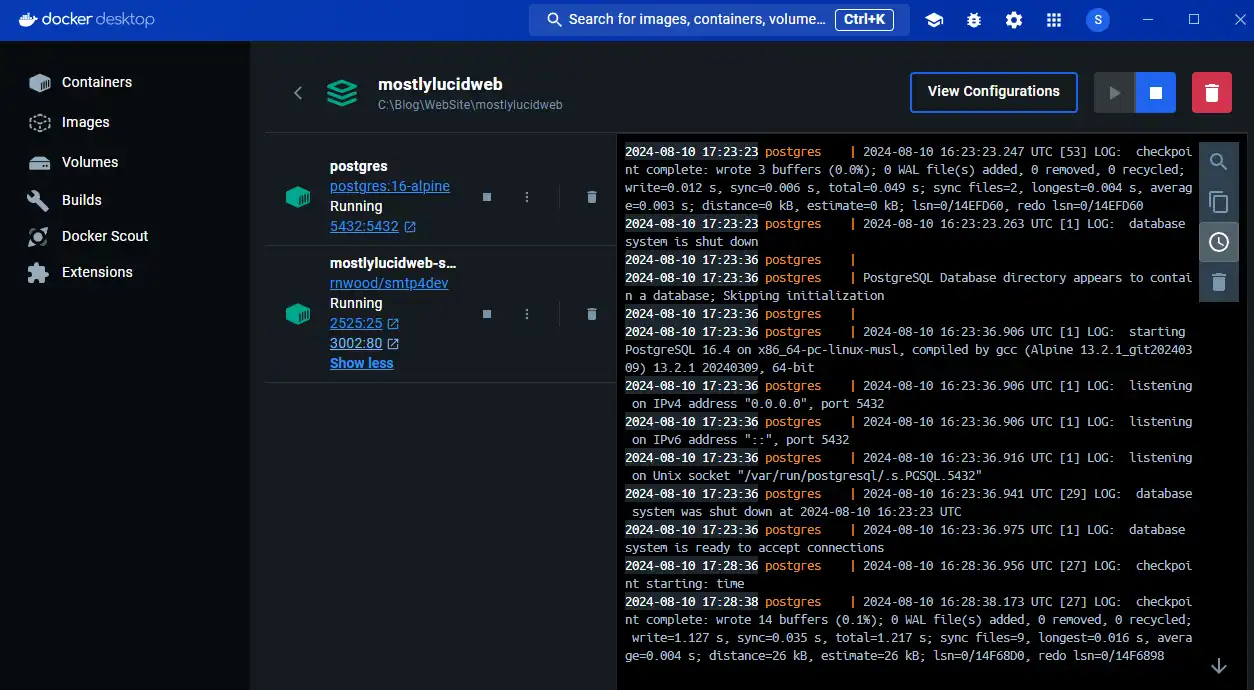
Docker Compose uses a YAML file to define the services you want to run. Here's an example of a simple devdeps-docker-compose.yml file that defines a database service and an Email service:
services:
smtp4dev:
image: rnwood/smtp4dev
ports:
- "3002:80"
- "2525:25"
volumes:
# This is where smtp4dev stores the database..
- e:/smtp4dev-data:/smtp4dev
restart: always
postgres:
image: postgres:16-alpine
container_name: postgres
ports:
- "5432:5432"
env_file:
- .env
volumes:
- e:/data:/var/lib/postgresql/data # Map e:\data to the PostgreSQL data folder
restart: always
networks:
mynetwork:
driver: bridge
Note here I've specified volumes for persisting the data for each service, here I've specified
volumes:
# This is where smtp4dev stores the database..
- e:/smtp4dev-data:/smtp4dev
volumes:
- e:/data:/var/lib/postgresql/data # Map e:\data to the PostgreSQL data folder
This ensures the data is persisted between runs of the containers.
I also specify an env_file for the postgres service. This is a file that contains environment variables that are passed to the container.
You can see a list of environment variables that can be passed to the PostgreSQL container here.
Here's an example of a .env file:
POSTGRES_DB=postgres
POSTGRES_USER=postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD=<somepassword>
This configures a default database, password and user for PostgreSQL.
Here I also run the SMTP4Dev service, this is a great tool for testing email functionality in your application. You can find more information about it here.
If you look in my appsettings.Developmet.json file you'll see I have the following configuration for the SMTP server:
"SmtpSettings":
{
"Server": "localhost",
"Port": 2525,
"SenderName": "Mostlylucid",
"Username": "",
"SenderEmail": "[email protected]",
"Password": "",
"EnableSSL": "false",
"EmailSendTry": 3,
"EmailSendFailed": "true",
"ToMail": "[email protected]",
"EmailSubject": "Mostlylucid"
}
This works for SMTP4Dev and it enables me to test this functionality (I can send to any address, and see the email in the SMTP4Dev interface at http://localhost:3002/).
Once you're sure it's all working you can test on a real SMTP server like GMAIL (e.g., see here for how to do that)
To run the services defined in the devdeps-docker-compose.yml file, you need to run the following command in the same directory as the file:
docker compose -f .\devdeps-docker-compose.yml up -d
Note you should run it initially like this; this ensures you can see the config elements passed in from the .env file.
docker compose -f .\devdeps-docker-compose.yml config
Now if you look in Docker Desktop you can see these services running